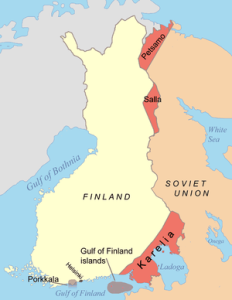
The Moscow Armistice was signed between Finland on one side and the Soviet Union and United Kingdom on the other side on September 19, 1944, ending the Continuation War. The Armistice restored the Moscow Peace Treaty of 1940, with a number of modifications.
Finland was obliged to cede parts of Karelia and Salla, as well as certain islands in the Gulf of Finland. The new armistice also handed all of Petsamo to the Soviet Union, and Finland was further compelled to lease Porkkala to the Soviet Union for a period of fifty years (the area was returned to Finnish control in 1956).
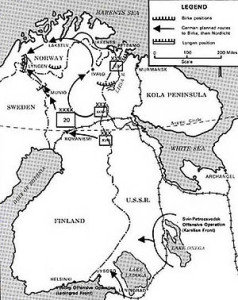
Germany and Finland had been at war with the Soviet Union since June 1941, co-operating closely in the Continuation War. However, as early as the summer of 1943, the German High Command began making plans for the eventuality that Finland might make a separate peace agreement with the Soviet Union. The Germans planned to withdraw their forces northward in order to shield the nickel mines near Petsamo.
During the winter of 1943–1944, the Germans improved the roads from northern Norway to northern Finland by extensive use of prisoner of war (POW) labour in certain areas. Casualties among these POWs were high, in part because many of them had been captured in southern Europe and were still in summer uniform. In addition, the Germans surveyed defensive positions and made plans to evacuate as much material as possible from the region and made meticulous preparations for withdrawing their forces. On 9 April 1944, the German withdrawal was named “Operation Birke”.
A change of Finnish leadership in early August 1944 led the Germans to believe that Finland would attempt to achieve a separate agreement with the Soviet Union. The Finnish announcement of the ceasefire triggered frantic efforts in the German 20th Mountain Army, which immediately started Operation Birke and other material evacuations from Finland. Large amounts of materiel were evacuated from southern Finland and harsh punishments were set for any hindering of the withdrawal. Finnish forces, which included the 3rd, 6th, and 11th divisions, the armoured division as well as the 15th and Border Jaeger brigades, were moved to face the Germans.
The cease fire agreement between Finland and the Soviet Union contained requirements that the Finns break diplomatic ties with Germany and publicly demand the withdrawal of all German troops from Finland by 15 September 1944. Any troops remaining after the deadline were to be disarmed and handed over to the Soviet Union. Even with the massive efforts of the Germans in Operation Birke, this proved impossible, with the Finns estimating it would take the Germans three months to fully evacuate. The task was further complicated by the Soviet demand that the major part of Finland’s armed forces be demobilized, even as they attempted to conduct a military campaign against the Germans. With the exception of the inhabitants of the Tornio area, most of the civilian population of Lapland (totaling 168,000 people) was evacuated to Sweden and Southern Finland. The evacuation was carried out as a cooperative effort between the German military and Finnish authorities prior to the start of hostilities.
From the start of the war the Germans had been systematically destroying and mining the roads and bridges as they withdrew. However, after the first real fighting took place the German commander, General Lothar Rendulic, issued several orders with regards to destroying Finnish property in Lapland.
On 6 October a strict order was issued which named only military or militarily important sites as targets. On 8 October, after the result of the fighting in Tornio and the Kemi region became obvious, the Germans made several bombing raids, targeting factory areas of Kemi and inflicting heavy damage on them. However, on 9 October the demolition order was extended to include all governmental buildings with the exception of hospitals. On 13 October, all habitable structures, including barns, though making an exception for hospitals and churches, were ordered to be destroyed north of the line running from Ylitornio via Sinettä (the small village ~20 km NWN of Rovaniemi) to Sodankylä (including the listed settlements) in northern Finland. Though it made sense from the German perspective to do this to deny pursuing forces from getting any shelter it had a very limited effect on the Finns who, unlike the Germans, always carried tents with them and did not require any existing shelter.
At Rovaniemi the Germans initially concentrated mainly on destroying governmental buildings but once fire got loose several more were destroyed. German attempts to fight the fire, however, failed and a train loaded with ammunition caught fire at Rovaniemi railroad station on 14 October resulting in a massive explosion which caused further destruction as well as spreading the fire throughout the primarily wooden buildings of the town. German attempts to fight the fire had failed by the time, on 16 October, they abandoned the now ruined town to the advancing Finns.
In their retreat the German forces under General Lothar Rendulic devastated large areas of northern Finland with scorched earth tactics. As a result, some 40–47% of the dwellings in the area were destroyed, and the provincial capital of Rovaniemi was burned to the ground, as were the villages of Savukoski and Enontekiö. Two-thirds of the buildings in the main villages of Sodankylä, Muonio, Kolari, Salla and Pello were demolished, 675 bridges were blown up, all main roads were mined, and 3,700 km of telephone lines were destroyed.